Dermatitis Treatments from U.S. Dermatology Partners
What Is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis, also sometimes referred to as eczema, is a common condition characterized by an itchy rash and inflamed skin. There are many different types of dermatitis and symptoms can range in severity from mild itching and redness to severe blistering and cracked skin.
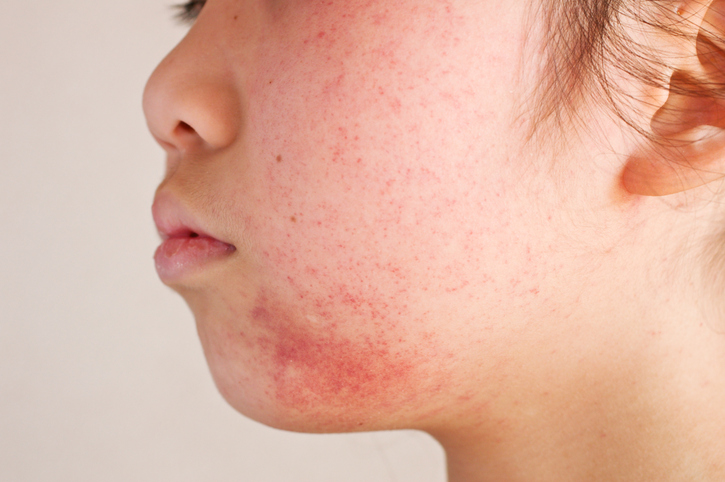
Dermatitis is a group of diseases and comes in many forms, but all are characterized by inflammation of the skin, redness and itchiness.
Find This Service Near You
Who Is at Risk for Dermatitis?
Dermatitis affects men, women and children of all ages. Though the exact causes of dermatitis are unknown, there are some factors that can increase your risk of developing certain types of dermatitis.
In some cases, dermatitis is known to run in families, indicating a possible genetic component. Other factors could include allergies, an overactive immune system, health conditions like congestive heart failure, Parkinson’s disease or HIV, contact with irritating substances or fabrics, stress and even extreme temperatures.
Dermatitis Symptoms
While dermatitis is really a group of diseases rather than a single one, it typically presents as a rash on the skin. The most common symptoms of dermatitis are itching, scaling, redness, fluid-filled blisters and cracking of the skin. The itchy redness can appear anywhere on the body, but most commonly affects the elbows, wrists, face, neck, knees, ankles and groin.
Dermatitis Treatment
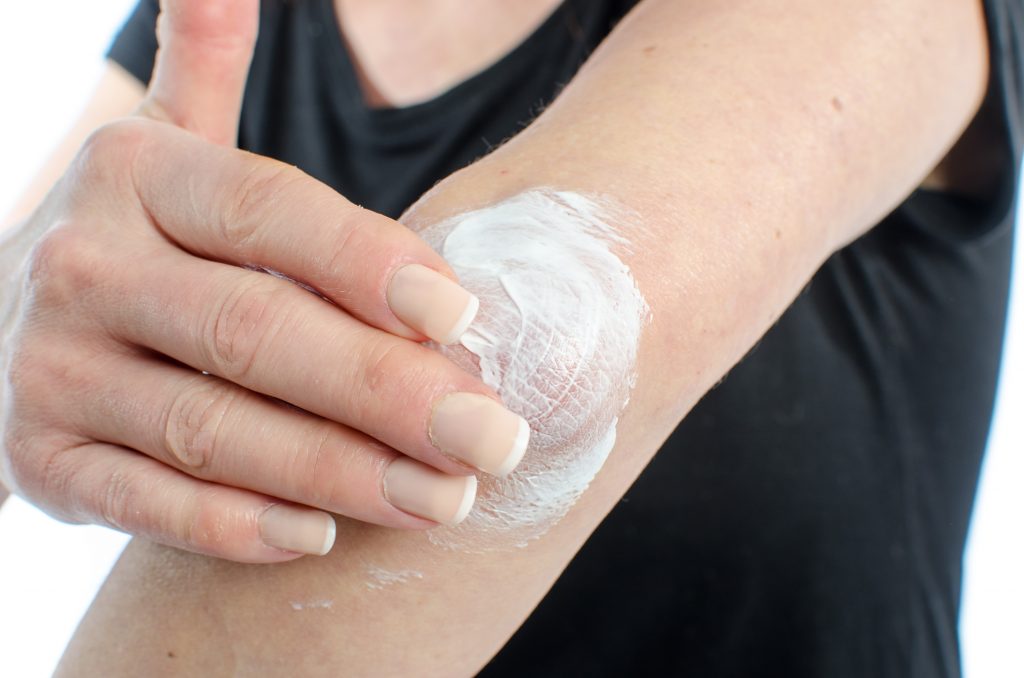
Applying moisturizer is recommended for preventing dermatitis flare-ups.
Treatments will vary depending on the cause and severity of the dermatitis, but using a mild soap at home that does not dry your skin and a high quality lotion after washing is recommended. Some tips for avoiding flare-ups include:
- Use lukewarm water and a mild, moisturizing soap.
- Apply moisturizer at least once a day.
- Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing.
- Avoid irritating fabrics such as wool against your skin.
If dermatitis is severe or persists, your doctor may recommend a topical corticosteroid or over-the-counter cream, as well as prescription ointments and an oral steroid. In the most severe cases, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic, an oral antihistamine (if an additional skin infection is suspected) or even topical immunosuppressant drugs to suppress an overactive immune system, though this is less common.
Dermatitis Prevention
The best way to prevent dermatitis is to avoid dry skin and known irritants. Use warm water instead of hot (which can irritate your skin), regularly use moisturizers, and choose mild, fragrance-free soaps.
*Results may vary by individual
