Skin cancer is one of the most severe and life-threatening concerns addressed by dermatologists, and we take the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of this condition very seriously. When it comes to offering effective skin cancer treatment, Dr. Leon Chen of U.S. Dermatology Partners Medical District in Houston, Texas, says, “Teaching our patients how to recognize skin cancer can be the difference between their receiving an early, treatable diagnosis and a late-stage diagnosis when treatment is much more invasive.” You can learn more about recognizing skin cancer in early stages in this blog, but don’t forget to ask your dermatologist to walk you through regular skin health self-exams during your next appointment.
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a condition that causes the uncontrolled proliferation of unhealthy cells. The healthy cells in our bodies replicate in a specific and orderly way. Cancer damages cellular DNA, which causes the cells to reproduce too quickly, in greater numbers, and otherwise leads to disorganized cellular reproduction.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
There are many causes of skin cancer, but sun exposure is the most common. Specifically, UV radiation from sunlight damages skin cells, leading to the replication of mutated cancer cells. In addition to sun exposure, some of the most common causes of skin cancer include:
- Chemical and toxin exposure
- X-rays or other exposure to radiation
- Burns or injuries, especially if they cover large areas of the skin
- Long-term use of medications that suppress the immune system
- Medical conditions that suppress the immune system
Related: What Happens if you Let Skin Cancer go Untreated?
Are there Different Types of Skin Cancer?
According to Dr. Chen, “There are many types of skin cancer and they are usually categorized as melanoma versus non-melanoma skin cancers. Melanomas develop when the cells that give the skin its tan color start to grow out of control. Although less common than non-melanoma skin cancers, melanomas are more dangerous as they are much more likely to spread to other parts of the body. In contrast, non-melanoma skin cancers are far more common and develop in the outermost layer of skin (epidermis).”
There are three main types of skin cancers:
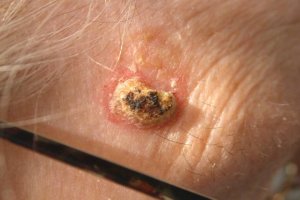
- Basal Cell Carcinoma – This is the most common type of non-melanoma skin cancer but is the least likely to spread or become life-threatening. However, without proper treatment, basal cell carcinoma can become locally invasive and destroy the surrounding structures such as muscles or bones.
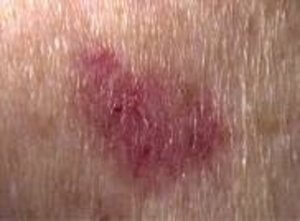
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma – Another common type of non-melanoma skin cancer that develops in the epidermis (outer layers) of skin cells, squamous cell carcinoma is more aggressive than basal cell carcinoma, and it is more likely to spread to other tissues and parts of the body without treatment.
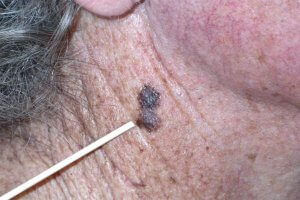
- Melanoma – The most serious and malignant form of skin cancer, melanoma is the cause of the majority (about 80%) of skin cancer-related deaths. Because melanoma may look like natural moles, freckles, and age spots, it can be overlooked in the earliest and most treatable stages.
What are the Symptoms of Skin Cancer?
Discussing the symptoms of skin cancer, Dr. Chen said, “Each type of skin cancer has a unique range of symptoms, and these warning signs often change as the condition progresses. We hope that, by keeping our patients informed about what they should be looking for in both early and late-stage skin cancers, we can start diagnosing these conditions in early stages and avoiding some of the more serious late-stage health consequences.” Below, we provide details about the early and late-stage symptoms of the three main types of skin cancer.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Early Stage Symptoms
In the early stages, multiple nests of basal cell carcinoma can be seen budding off the basal layer of the epidermis (outer layer) at a superficial level. As it progresses, the tumor may grow to be about the size of a peanut, and it may spread and invade deeper in the dermis. This type of skin cancer can develop anywhere, but it is most prevalent in the areas that receive the greatest amount of sun exposure, including the face, hands, scalp, ears, legs, arms, and shoulders.
Basal cell carcinoma early-stage symptoms may include:
- A small, round growth that may be red, pink, brown, black, or match your skin tone in color. It may be shiny and has fine blood vessels on it.
- The growth may have a dip or concave portion in the middle
- A scaly, dry patch of skin
- A sore that doesn’t heal
- Sores that heal and reopen, bleed, or ooze
- A raised area of irritated skin
- A scar-like growth that makes surrounding skin feel tight
- A spot in the skin that feels numb or has a pins-and-needles sensation
Basal Cell Carcinoma Late Stage Symptoms
In the later stages of basal cell carcinoma, you’ll see the tumor and affected area of skin growing. In addition to negatively impacting the epidermis and dermis, basal cell carcinoma may spread into other tissues and organs. You may see the original tumor or skin growth begin to evolve quickly or spread to cover a larger area. You may also notice swelling and inflammation in the lymph nodes near the tumor site.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Early Stage Symptoms
Squamous cell carcinoma can develop in any of the body’s squamous cells, including those that make up parts of the skin. In the early stages, this condition will typically impact just the outermost skin layers, but it is more likely than basal cell carcinoma to spread into the deeper dermis layers and surrounding tissues. Like basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma usually forms on the parts of the body that are most exposed to sunlight like the face, ears, scalp, lips, hands, legs, and arms. In addition to these often sun-exposed areas, squamous cell carcinoma can also develop inside the mouth, around the genitals and anus, or under the fingernails and toenails.
Squamous cell carcinoma early-stage symptoms may include:
- The appearance of scaly or crusty pre-cancerous lesions known as actinic keratosis
- A scaly patch of skin that is typically red or pink but may be white, yellow, brown, or black or have spots of darker coloring within a red or pink colored patch
- A spot on the skin that looks like an age spot, but it may be growing, have an uneven border, or have a texture that is different from surrounding skin
- An open sore that doesn’t heal or that reopens
- A firm growth that looks like a small dome, wart, or horn
- Scar tissue that suddenly develops a new sore
- Inside the mouth, squamous cell carcinoma usually has a different texture than surrounding tissue and may form small sores
- Around the genitals and anus, you may see raised patches, sores, or wart-like growths
- Around the nails, you might notice darkening of the skin beneath the nail or sores forming in the cuticles and beneath the nails
- Growths may also itch, feel numb, or cause skin tenderness or discomfort
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Late Stage Symptoms
According to Dr. Chen, “Only about 5% of squamous cell carcinomas reach the advanced stages. When these tumors are untreated, resistant to treatment, or spread into surrounding tissues or organs, the squamous cell carcinoma is considered to be advanced, and at this stage, more advanced treatment may be required.” This advanced form of squamous cell carcinoma may be localized, which means it impacts the skin, tissues, muscles, bones, and organs in the immediate area surrounding the tumor. It may also metastasize meaning it spreads to parts of the body that are not directly connected to the original tumor. Depending on the extent of the condition, you may experience a wide range of symptoms, but the most noticeable is usually the developments or changes within the originally impacted area. You may see the tumor getting larger, changing shape, or otherwise evolving. Swelling in the lymph nodes is also a common sign of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma Early Stage Symptoms
Melanoma is the most serious and life-threatening form of skin cancer. It is more likely to spread into surrounding tissue and metastasize damaging unconnected tissue and organs. For this reason, it’s very important to recognize melanoma in its early stages and seek medical treatment right away. Melanoma can look like a mole, freckle, or age spot. Many people overlook these new melanoma spots until the condition becomes more serious. In order to spot melanoma in its earliest stages, you should conduct regular skin self-exams and note the ABCDE’s of melanoma skin cancer:
- A – Asymmetry – One side of the mole is different from the other in size, shape, color, or texture.
- B – Border – The edges of the mole are uneven or irregular.
- C – Color – The mole may be inconsistently colored or be a color unlike other moles on the body.
- D – Diameter – The mole is larger in diameter than an eraser or it’s growing quickly.
- E – Evolution – Any rapid change in color, texture, size, or shape can be indicative of melanoma.
Melanoma Late Stage Symptoms
Unfortunately, melanoma is more likely to grow and spread rapidly than other forms of skin cancer, so we see more cases of advanced-stage melanoma. Melanoma is also more likely to metastasize, meaning it can spread to any part of the body, but it is most often spreads to the lymph nodes, bones, lungs, liver, and brain.
Melanoma late-stage symptoms include:
- Swollen or hardened lymph nodes
- Hard lumps under the skin
- General ill health – tiredness, unexplained pain, fatigue, fever
- Weight loss that is unrelated to changes in diet or exercise routines
- Jaundice – yellowing eyes or skin
- Swelling in the stomach due to a build-up of fluid
What Should I Do if I Notice Signs of Skin Cancer?
If you think you’ve discovered any sign of skin cancer, you should contact your dermatologist right away. The sooner we confirm your diagnosis and begin treatment, the better. In the early stages, we can often provide minimally invasive treatments to fully remove the tumor and damaged skin cells. Once skin cancer begins to spread into surrounding tissues or metastasize and affect other parts of the body, we will need to create a more aggressive and potentially invasive treatment plan.
Can I Prevent Skin Cancer?
According to Dr. Chen, “Performing regular skin exams and visiting our office at least once a year for a are the best and easiest things you can do to minimize your risk for skin cancer.” In addition to regular skin cancer screenings, you should also take steps to avoid exposure to chemicals, toxins, radiation, and other causes of skin cancer. And most importantly, you should protect your skin daily from the sun’s damaging UVA/B rays by applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to areas of the skin that may be exposed to the sun.
When Should I Schedule a Visit with U.S. Dermatology Partners?
Whether it’s time for your annual skin exam or you’re concerned about something you noticed during your regular self-exams, the U.S. Dermatology Partners team looks forward to providing you with exemplary care. You can schedule an in-office visit with one of our skilled dermatologists by filling out a simple request form online. A team member will be in touch to verify your appointment details soon.
If you prefer to chat with one of our knowledgeable dermatologists online, we’re happy to offer teledermatology appointments. Simply fill out our virtual visit request form, and we’ll be in touch to confirm your appointment.
Find a location near me
or