As we continue to promote understanding and improved skin care this Skin Cancer Awareness Month, we want to share a little more about diagnosis and treatment options for different types of skin cancer. Keep reading to learn about the multitude of skin cancer treatment options available to renew your health after a skin cancer diagnosis.
Skin Cancer Diagnosis
In most cases, the diagnosis of skin cancer begins with a simple visual examination. We will look at the area of concern and discuss your past health history, especially as it relates to skin health and cancer. In addition to your personal history, we will discuss your family’s health history. If we identify any lesions suspicious for skin cancer, we will perform a biopsy. During the biopsy, we remove the skin lesion and send it for microscopic testing. This microscopic examination will identify the type of cancer cells and give us guidance on treatment options. After diagnosis, we will create a treatment plan which may involve surgery or a number of other procedures.
Skin Cancer Treatment Options
In most cases, a skin cancer treatment plan will involve some form of surgery to remove the damaged skin cells. Typically, we recommend Mohs micrographic surgery, electrodessication, and curettage, or a topical chemotherapy cream. We may also perform:
- Simple excision – cutting away the tumor and surrounding tissue to protect the rest of your body.
- Shave excision – the abnormal cells are shaved off the skin’s surface.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery
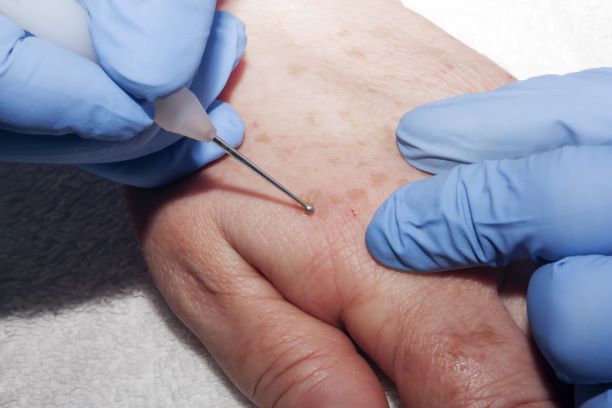
In use since the 1930s, Mohs micrographic surgery is still one of the most effective treatment options for treating certain types of skin cancers. It can be a lengthy process, but it ensures the removal of all the cancerous skin cells while preserving the maximum amount of healthy tissue. During the procedure, abnormal skin cells are removed in layers. Throughout the process, the tumor and surrounding skin are examined microscopically to determine if all cancerous cells have been removed. The process continues until only healthy cells remain. Because Mohs surgery preserves the maximum amount of healthy tissue possible, it is the ideal solution for skin in the most sensitive areas like the face, hands, and genitals.
Electrodessication and Curettage
Electrodessication and curettage involve the removal of abnormal cells using a curette. A curette is a small, sharp, spoon-like tool that can precisely remove the damaged tissue. Then, an electrode sends an electric current to cauterize the area.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation is a common cancer therapy that is utilized as a part of treatment plans for all types of cancer. There are both external and internal radiation therapies. External radiation uses a machine to administer radiation drugs that target specific areas of cancerous cells and destroy them. Internal radiation therapy places a radioactive substance directly onto the cancerous area, using needles, wires, and other local delivery systems.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to prevent the growth or division of cancer cells. The chemotherapy drugs may be administered via oral pill or intravenous injection, allowing the drugs to spread throughout the body. For more localized concerns, regional chemotherapy may be administered into the organs or general area of concern to limit the common side effects of chemotherapy. Localized chemotherapy treatments can be injected, but many skin cancer patients actually receive chemotherapy through a topical cream or ointment.
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a unique form of cancer treatment that combines a light-activated medication that is either injected intravenously or applied topically with laser light treatment. Once exposed to light, the medication activates killing the cancer cells. Because these medications accumulate in much higher numbers in the cancer cells, healthy skin cells receive little to no damage.
Immunotherapy
Our immune system exists to protect our bodies from health issues, fighting off disease and infection. Immunotherapy utilizes the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. Drugs are used to enhance the body’s immune response, targeting cancer cells to prevent replication and promote the vitality and multiplication of healthy cells and tissues.
Cryosurgery
While many surgical techniques use heat to cauterize wounds, cryosurgery freezes cells. This allows us to target and destroy abnormal tissue, leaving healthy skin cells intact.
We Answer Your Skin Cancer Treatment Options Frequently Asked Questions
Our team at U.S. Dermatology Partners is always happy to answer your questions and help you with the diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer. Below, we’ve compiled answers to just a few of the most common questions.
What is the Best Treatment Option for Basal or Squamous Cell Skin Cancer?
There are many ways of treating basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer. Mohs surgery is the gold standard with the highest cure rates for treating skin cancer in highly sensitive areas such as the head, neck, hands, and feet. With Mohs surgery, we can examine 100% of the margins of the skin cancer to ensure complete removal. For less sensitive areas such as the back and the arms, standard excision or electrodesiccation and curettage are often effective options.
Why is Mohs Surgery not Typically a Treatment for Melanoma?
Mohs surgery is widely considered to be the best skin cancer surgical treatment option, but it is not typically recommended for those who have been diagnosed with melanoma. Mohs surgery for melanoma is still a controversial topic. In melanoma, the pigment-producing cells in the skin (also known as melanocytes) have mutated to become malignant. Some experts believe that these cells are harder to identify via traditional Mohs surgery techniques. Other experts also believe that the way melanoma spreads very quickly and not contiguously make it an unfavorable candidate for Mohs surgery.
What Risks are Associated with Forgoing Skin Cancer Treatment?
We always recommend treatment in the earliest stages to avoid the growth or spread of skin cancer. If basal cell carcinoma is not treated, it will continue to grow locally and cause destruction to the surrounding tissues. This can be very deforming, painful, and may even cause death in rare circumstances. If squamous cell carcinoma is not treated, it will also continue to grow locally. Some types of squamous cell carcinoma also have a high risk of spreading to other organs. Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, and without removal, it can quickly spread to surrounding tissues and bodily systems.
Let U.S. Dermatology Partners Help with your Skin Cancer Treatment Options
If you are concerned about an abnormal mole or spot, the team at U.S. Dermatology Partners can help you with skin cancer prevention, diagnosis, and treatment planning. Simply complete our online form to request an appointment with a dermatologist near you. One of our local offices will be in touch with you to answer questions and schedule your visit.
Find a location near me
or