Derm Access Program
Locations | FAQ | Request Derm Access
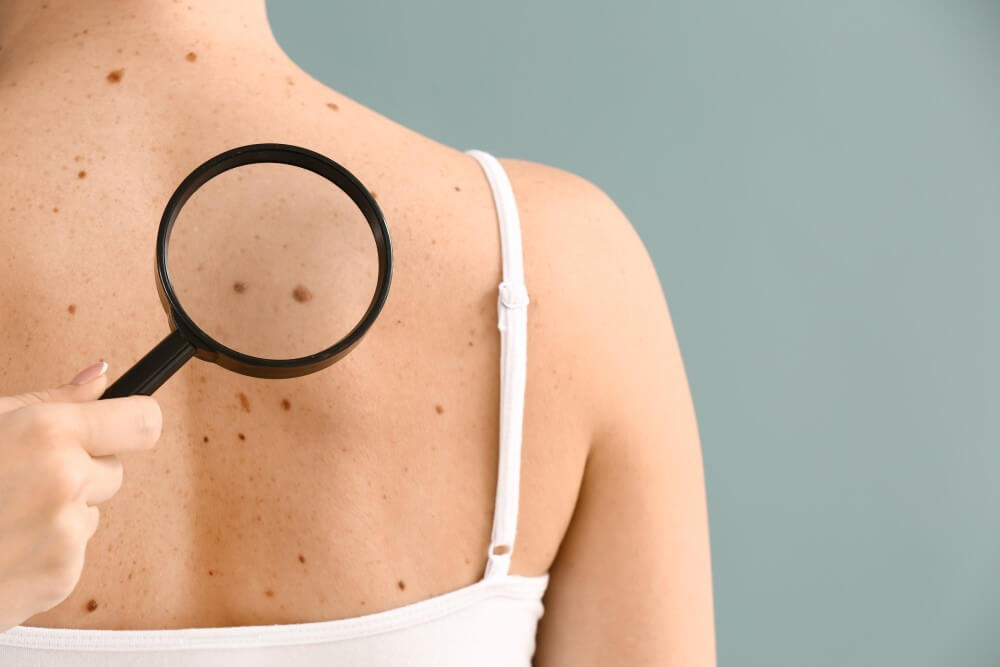
U.S. Dermatology Partners is proud to offer the Derm Access Program to our communities. Derm Access is a program designed to increase the accessibility of skin cancer screenings. This program allows a single spot of concern to be evaluated within 72 hours. Don’t ignore suspicious or changing spots on your skin. Contact our nearest office to request a derm access appointment. 1515 Medical Pkwy, Bldg 1, #100 11550 Granada Ln 8380 N Tullis Ave 3265 NE Ralph Powell Road 17067 S Outer Road #200 A program designed to increase accessibility of skin cancer screenings, allowing suspicious lesions to be evaluated within 72 hours. There is a shortage of board-certified dermatologists so the wait time to be seen can be lengthy coupled with the increase in the incidence of skin cancers diagnosed annually. If you have a patient with a lesion that is changing or of concern, we know it can be troubling to wait to be seen. Early detection is key to successfully treating skin cancer. Any patient with a lesion that is growing or evolving. If your patient has a mole or spot that is bleeding, not healing, changing, growing in size or color, or a previous skin cancer diagnosis and the lesion is reminiscent of what they have had before, patients can call and be worked in to be seen as a priority. Derm Access appointments should not be considered a substitute for a full-body skin examination performed by a board-certified dermatologist. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that patients receive a full-body skin exam annually.Early Detection is Key in the Fight Against Skin Cancer
Locations Offering Derm Access
U.S. Dermatology Partners Cedar Park
Cedar Park, TX 78613
(512) 690-4942
Book Derm AccessU.S. Dermatology Partners Leawood
Leawood, KS 66211
(913) 451-7546
Request Derm AccessU.S. Dermatology Partners Kansas City Shoal Creek
Kansas City, MO 64158
(816) 524-4747
Request Derm AccessU.S. Dermatology Partners Lee’s Summit
Lee’s Summit, MO 64064
(816) 454-3424
Request Derm AccessU.S. Dermatology Partners Belton MO
Belton, MO 64012
(816) 630-7546
Request Derm Access
Did You Know?
FAQ
What is Derm Access?
Why is Derm Access Important?
Who Qualifies for a Derm Access Appointment?
What puts patients at an increase of Skin Cancer?